parse 函数
模版 AST
对于如下模版
js
<div>
<h1 v-if="ok" class="test">
Vue Template {{ msg }}
</h1>
</div><div>
<h1 v-if="ok" class="test">
Vue Template {{ msg }}
</h1>
</div>这段模板会被编译为如下所示的 AST:
js
const ast = {
type: 0, // ROOT
children: [
{
type: 1, // ELEMENT
tag: 'div',
tagType: 0,
props: [],
children: [
{
type: 1, // ELEMENT
tag: 'h1',
tagType: 0,
props: [
{
type: 7, // DIRECTIVE
name: 'if',
exp: {
type: 4, // SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
content: 'ok',
isStatic: false,
loc: {},
},
loc: {},
},
{
type: 6, // ATTRIBUTE
name: 'class',
value: {
type: 2, // TEXT
content: 'test',
loc: {},
},
loc: {},
},
],
children: [
{
type: 2, // TEXT
content: 'Vue Template ',
},
{
type: 5, // INTERPOLATION
content: {
type: 4, // SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
isStatic: false,
content: 'msg',
},
},
],
},
],
},
],
loc: {},
};const ast = {
type: 0, // ROOT
children: [
{
type: 1, // ELEMENT
tag: 'div',
tagType: 0,
props: [],
children: [
{
type: 1, // ELEMENT
tag: 'h1',
tagType: 0,
props: [
{
type: 7, // DIRECTIVE
name: 'if',
exp: {
type: 4, // SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
content: 'ok',
isStatic: false,
loc: {},
},
loc: {},
},
{
type: 6, // ATTRIBUTE
name: 'class',
value: {
type: 2, // TEXT
content: 'test',
loc: {},
},
loc: {},
},
],
children: [
{
type: 2, // TEXT
content: 'Vue Template ',
},
{
type: 5, // INTERPOLATION
content: {
type: 4, // SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
isStatic: false,
content: 'msg',
},
},
],
},
],
},
],
loc: {},
};不同类型的节点是通过节点的 type 属性进行区分的。例如标签节点的 type 值为 'Element'。
标签节点的子节点存储在其 children 数组中。
标签节点的属性节点和指令节点会存储在 props 数组中。
不同类型的节点会使用不同的对象属性进行描述。例如指令节点拥有 name 属性,用来表达指令的名称,而表达式节点拥有 content 属性,用来描述表达式的内容。
词法分析,建立 Token 列表
伪代码
js
// 定义状态机的状态
const State = {
initial: 1, // 初始状态
tagOpen: 2, // 标签开始状态
tagName: 3, // 标签名称状态
text: 4, // 文本状态
tagEnd: 5, // 结束标签状态
tagEndName: 6, // 结束标签名称状态
};
// 一个辅助函数,用于判断是否是字母
function isAlpha(char) {
return (char >= 'a' && char <= 'z') || (char >= 'A' && char <= 'Z');
}
// 接收模板字符串作为参数,并将模板切割为 Token 返回
function tokenize(str) {
// 状态机的当前状态:初始状态
let currentState = State.initial;
// 用于缓存字符
const chars = [];
// 生成的 Token 会存储到 tokens 数组中,并作为函数的返回值返回
const tokens = [];
// 使用 while 循环开启自动机,只要模板字符串没有被消费尽,自动机就会一直运行
while (str) {
// 查看第一个字符,注意,这里只是查看,没有消费该字符
const char = str[0];
// switch 语句匹配当前状态
switch (currentState) {
// 状态机当前处于初始状态
case State.initial:
// 遇到字符 <
if (char === '<') {
// 1. 状态机切换到标签开始状态
currentState = State.tagOpen;
// 2. 消费字符 <
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,切换到文本状态
currentState = State.text;
// 2. 将当前字母缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 3. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于标签开始状态
case State.tagOpen:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,切换到标签名称状态
currentState = State.tagName;
// 2. 将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 3. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '/') {
// 1. 遇到字符 /,切换到结束标签状态
currentState = State.tagEnd;
// 2. 消费字符 /
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于标签名称状态
case State.tagName:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,由于当前处于标签名称状态,所以不需要切换状态,
// 但需要将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 2. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '>') {
// 1.遇到字符 >,切换到初始状态
currentState = State.initial;
// 2. 同时创建一个标签 Token,并添加到 tokens 数组中
// 注意,此时 chars 数组中缓存的字符就是标签名称
tokens.push({
type: 'tag',
name: chars.join(''),
});
// 3. chars 数组的内容已经被消费,清空它
chars.length = 0;
// 4. 同时消费当前字符 >
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于文本状态
case State.text:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,保持状态不变,但应该将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 2. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '<') {
// 1. 遇到字符 <,切换到标签开始状态
currentState = State.tagOpen;
// 2. 从 文本状态 --> 标签开始状态,此时应该创建文本 Token,并添加到 tokens 数组
// 注意,此时 chars 数组中的字符就是文本内容
tokens.push({
type: 'text',
content: chars.join(''),
});
// 3. chars 数组的内容已经被消费,清空它
chars.length = 0;
// 4. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于标签结束状态
case State.tagEnd:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,切换到结束标签名称状态
currentState = State.tagEndName;
// 2. 将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 3. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于结束标签名称状态
case State.tagEndName:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,不需要切换状态,但需要将当前字符缓存到 chars数组
chars.push(char);
// 2. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '>') {
// 1. 遇到字符 >,切换到初始状态
currentState = State.initial;
// 2. 从 结束标签名称状态 --> 初始状态,应该保存结束标签名称Token
// 注意,此时 chars 数组中缓存的内容就是标签名称
tokens.push({
type: 'tagEnd',
name: chars.join(''),
});
// 3. chars 数组的内容已经被消费,清空它
chars.length = 0;
// 4. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
}
}
// 最后,返回 tokens
return tokens;
}// 定义状态机的状态
const State = {
initial: 1, // 初始状态
tagOpen: 2, // 标签开始状态
tagName: 3, // 标签名称状态
text: 4, // 文本状态
tagEnd: 5, // 结束标签状态
tagEndName: 6, // 结束标签名称状态
};
// 一个辅助函数,用于判断是否是字母
function isAlpha(char) {
return (char >= 'a' && char <= 'z') || (char >= 'A' && char <= 'Z');
}
// 接收模板字符串作为参数,并将模板切割为 Token 返回
function tokenize(str) {
// 状态机的当前状态:初始状态
let currentState = State.initial;
// 用于缓存字符
const chars = [];
// 生成的 Token 会存储到 tokens 数组中,并作为函数的返回值返回
const tokens = [];
// 使用 while 循环开启自动机,只要模板字符串没有被消费尽,自动机就会一直运行
while (str) {
// 查看第一个字符,注意,这里只是查看,没有消费该字符
const char = str[0];
// switch 语句匹配当前状态
switch (currentState) {
// 状态机当前处于初始状态
case State.initial:
// 遇到字符 <
if (char === '<') {
// 1. 状态机切换到标签开始状态
currentState = State.tagOpen;
// 2. 消费字符 <
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,切换到文本状态
currentState = State.text;
// 2. 将当前字母缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 3. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于标签开始状态
case State.tagOpen:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,切换到标签名称状态
currentState = State.tagName;
// 2. 将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 3. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '/') {
// 1. 遇到字符 /,切换到结束标签状态
currentState = State.tagEnd;
// 2. 消费字符 /
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于标签名称状态
case State.tagName:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,由于当前处于标签名称状态,所以不需要切换状态,
// 但需要将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 2. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '>') {
// 1.遇到字符 >,切换到初始状态
currentState = State.initial;
// 2. 同时创建一个标签 Token,并添加到 tokens 数组中
// 注意,此时 chars 数组中缓存的字符就是标签名称
tokens.push({
type: 'tag',
name: chars.join(''),
});
// 3. chars 数组的内容已经被消费,清空它
chars.length = 0;
// 4. 同时消费当前字符 >
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于文本状态
case State.text:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,保持状态不变,但应该将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 2. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '<') {
// 1. 遇到字符 <,切换到标签开始状态
currentState = State.tagOpen;
// 2. 从 文本状态 --> 标签开始状态,此时应该创建文本 Token,并添加到 tokens 数组
// 注意,此时 chars 数组中的字符就是文本内容
tokens.push({
type: 'text',
content: chars.join(''),
});
// 3. chars 数组的内容已经被消费,清空它
chars.length = 0;
// 4. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于标签结束状态
case State.tagEnd:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,切换到结束标签名称状态
currentState = State.tagEndName;
// 2. 将当前字符缓存到 chars 数组
chars.push(char);
// 3. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
// 状态机当前处于结束标签名称状态
case State.tagEndName:
if (isAlpha(char)) {
// 1. 遇到字母,不需要切换状态,但需要将当前字符缓存到 chars数组
chars.push(char);
// 2. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
} else if (char === '>') {
// 1. 遇到字符 >,切换到初始状态
currentState = State.initial;
// 2. 从 结束标签名称状态 --> 初始状态,应该保存结束标签名称Token
// 注意,此时 chars 数组中缓存的内容就是标签名称
tokens.push({
type: 'tagEnd',
name: chars.join(''),
});
// 3. chars 数组的内容已经被消费,清空它
chars.length = 0;
// 4. 消费当前字符
str = str.slice(1);
}
break;
}
}
// 最后,返回 tokens
return tokens;
}状态机
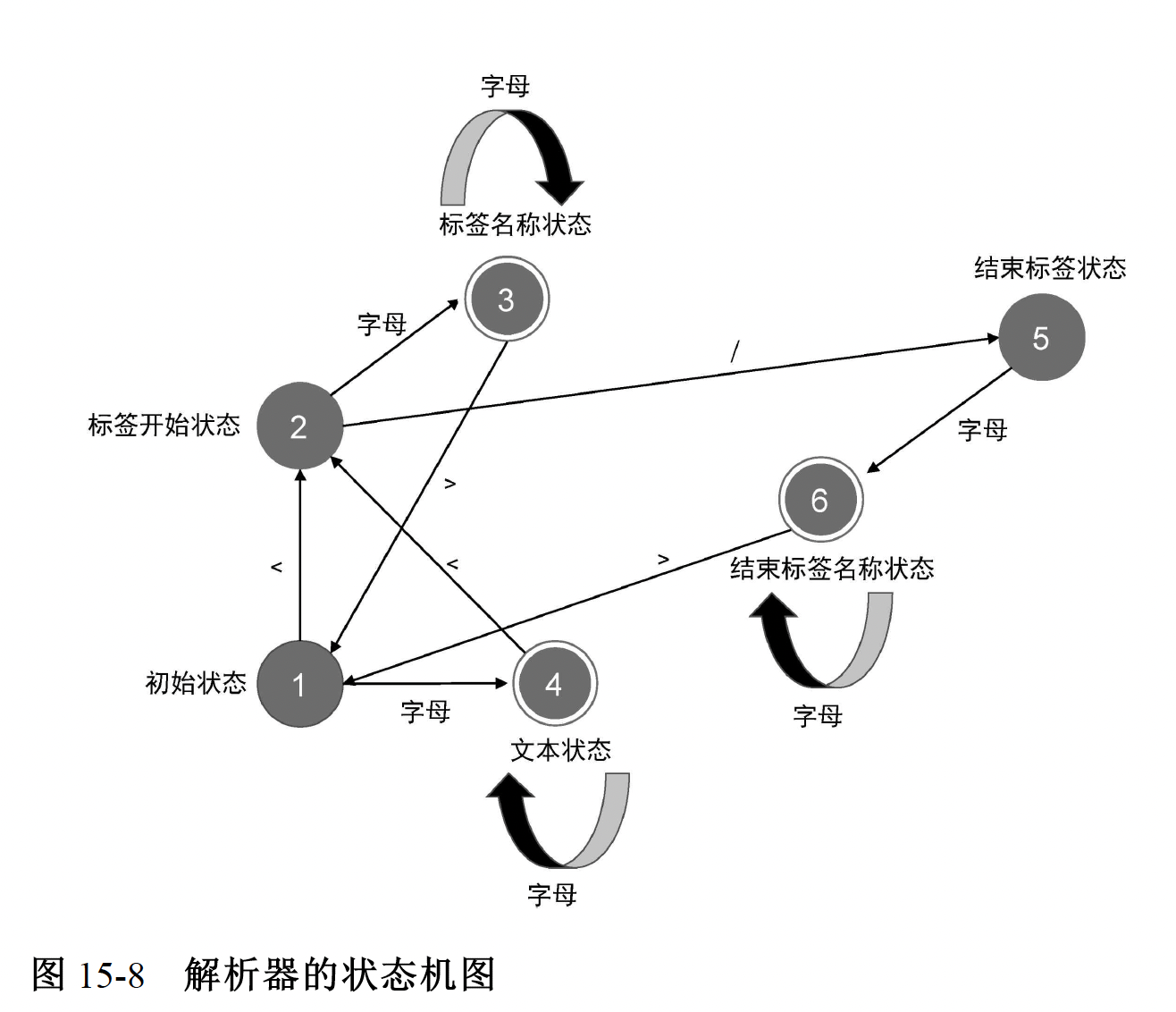
结果
这里的 type 和 vnode 的 type 不是一个意思
js
const tokens = tokenize(`<div><p>Vue</p><p>Template</p></div>`);
const tokens = [
{ type: 'tag', name: 'div' }, // div 开始标签节点
{ type: 'tag', name: 'p' }, // p 开始标签节点
{ type: 'text', content: 'Vue' }, // 文本节点
{ type: 'tagEnd', name: 'p' }, // p 结束标签节点
{ type: 'tag', name: 'p' }, // p 开始标签节点
{ type: 'text', content: 'Template' }, // 文本节点
{ type: 'tagEnd', name: 'p' }, // p 结束标签节点
{ type: 'tagEnd', name: 'div' }, // div 结束标签节点
];const tokens = tokenize(`<div><p>Vue</p><p>Template</p></div>`);
const tokens = [
{ type: 'tag', name: 'div' }, // div 开始标签节点
{ type: 'tag', name: 'p' }, // p 开始标签节点
{ type: 'text', content: 'Vue' }, // 文本节点
{ type: 'tagEnd', name: 'p' }, // p 结束标签节点
{ type: 'tag', name: 'p' }, // p 开始标签节点
{ type: 'text', content: 'Template' }, // 文本节点
{ type: 'tagEnd', name: 'p' }, // p 结束标签节点
{ type: 'tagEnd', name: 'div' }, // div 结束标签节点
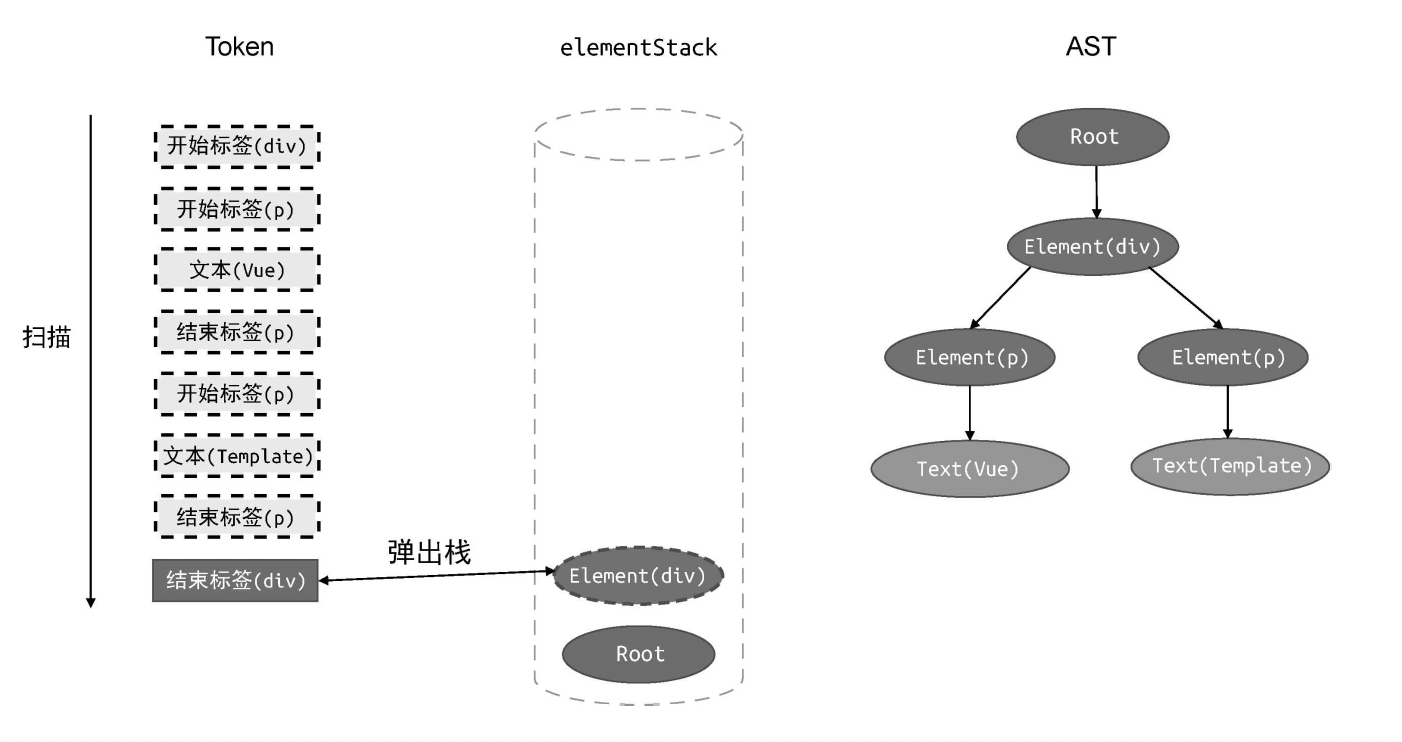
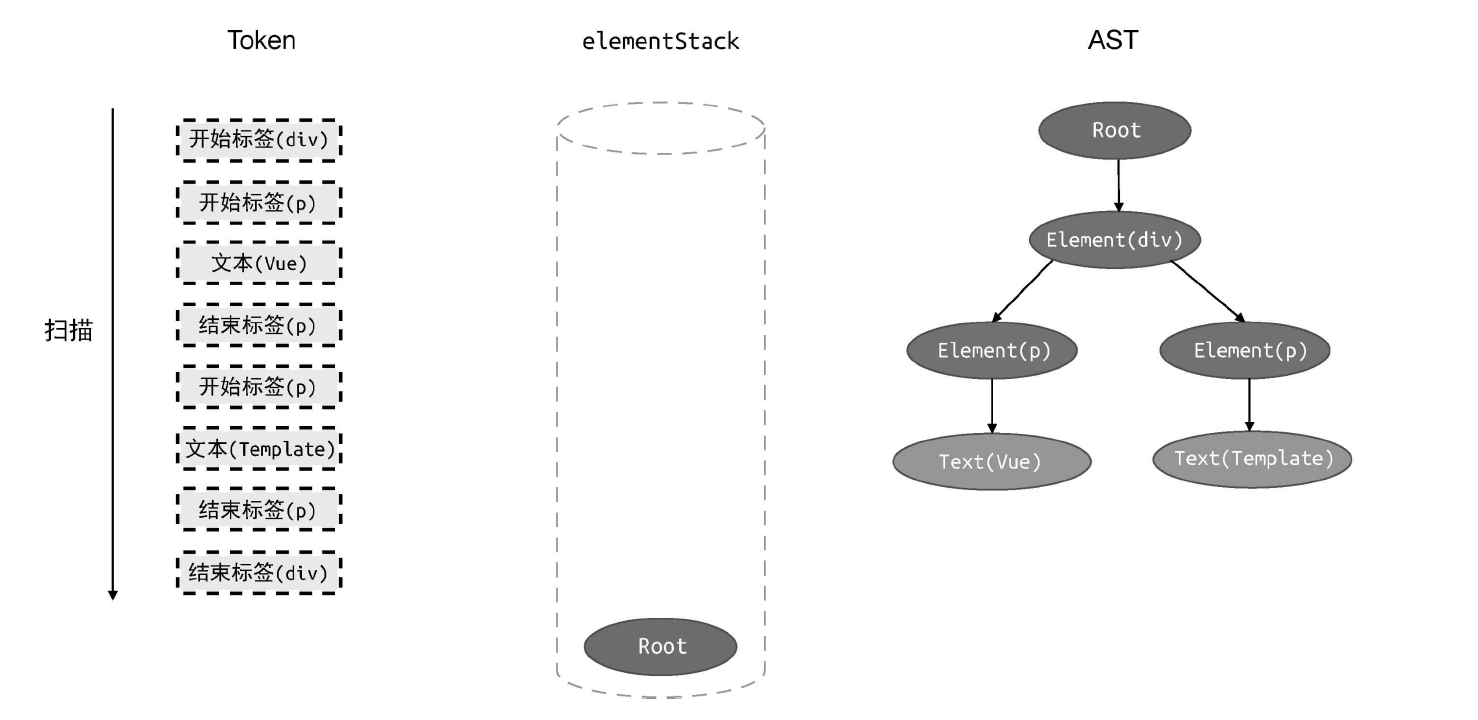
];建立 AST
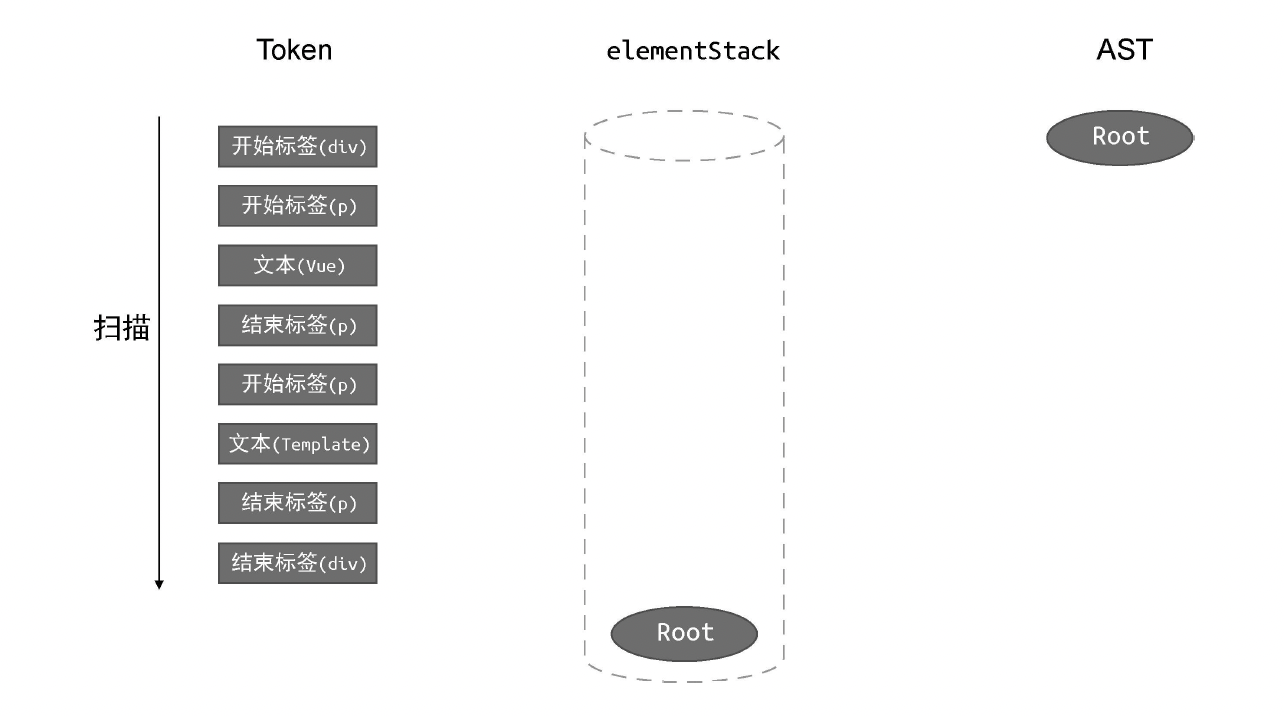
伪代码
js
// parse 函数接收模板作为参数
function parse(str) {
// 首先对模板进行标记化,得到 tokens
const tokens = tokenize(str);
// 创建 Root 根节点
const root = {
type: 'Root',
children: [],
};
// 创建 elementStack 栈,起初只有 Root 根节点
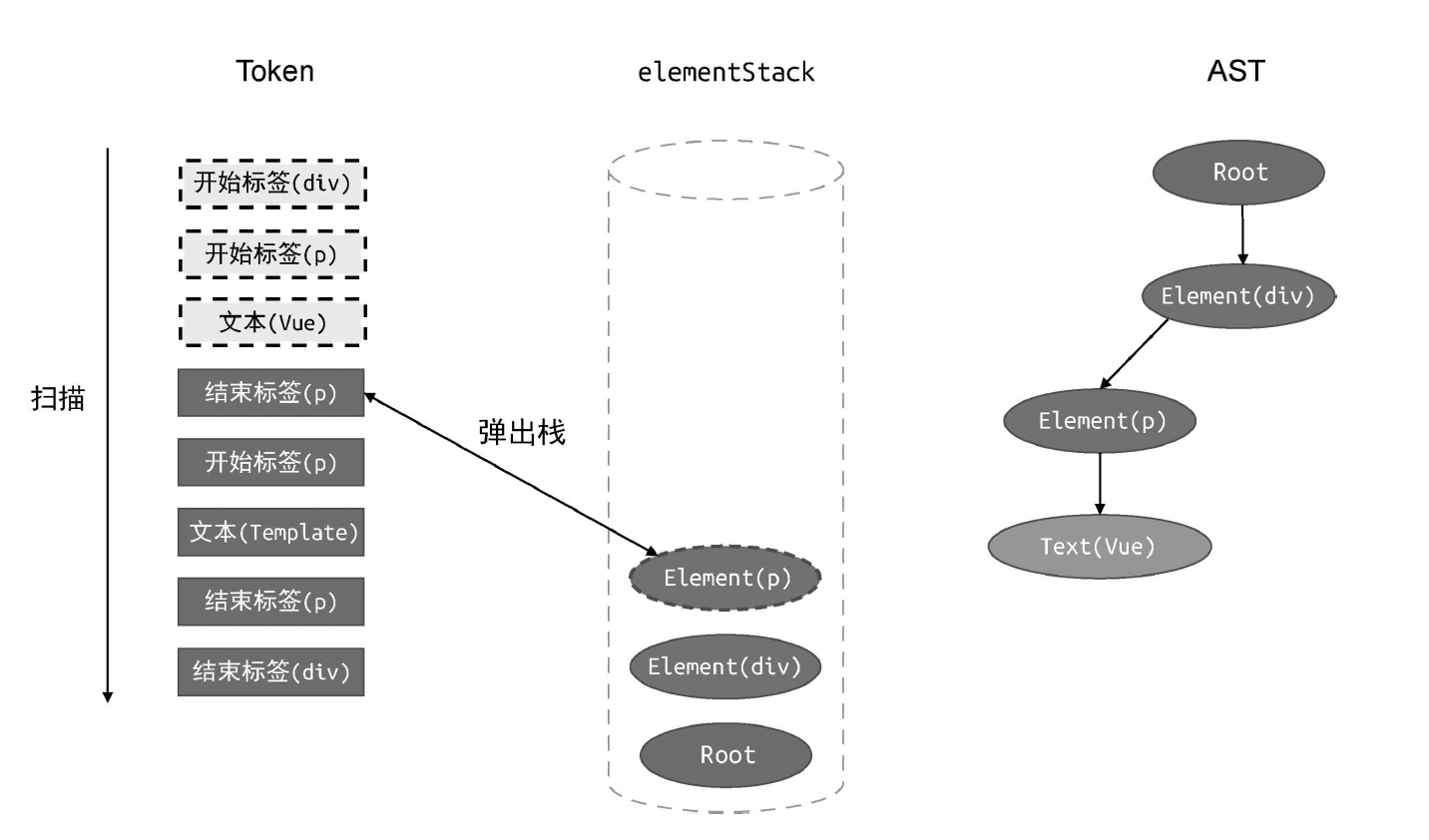
const elementStack = [root];
// 开启一个 while 循环扫描 tokens,直到所有 Token 都被扫描完毕为止
while (tokens.length) {
// 获取当前栈顶节点作为父节点 parent
const parent = elementStack[elementStack.length - 1];
// 当前扫描的 Token
const t = tokens[0];
switch (t.type) {
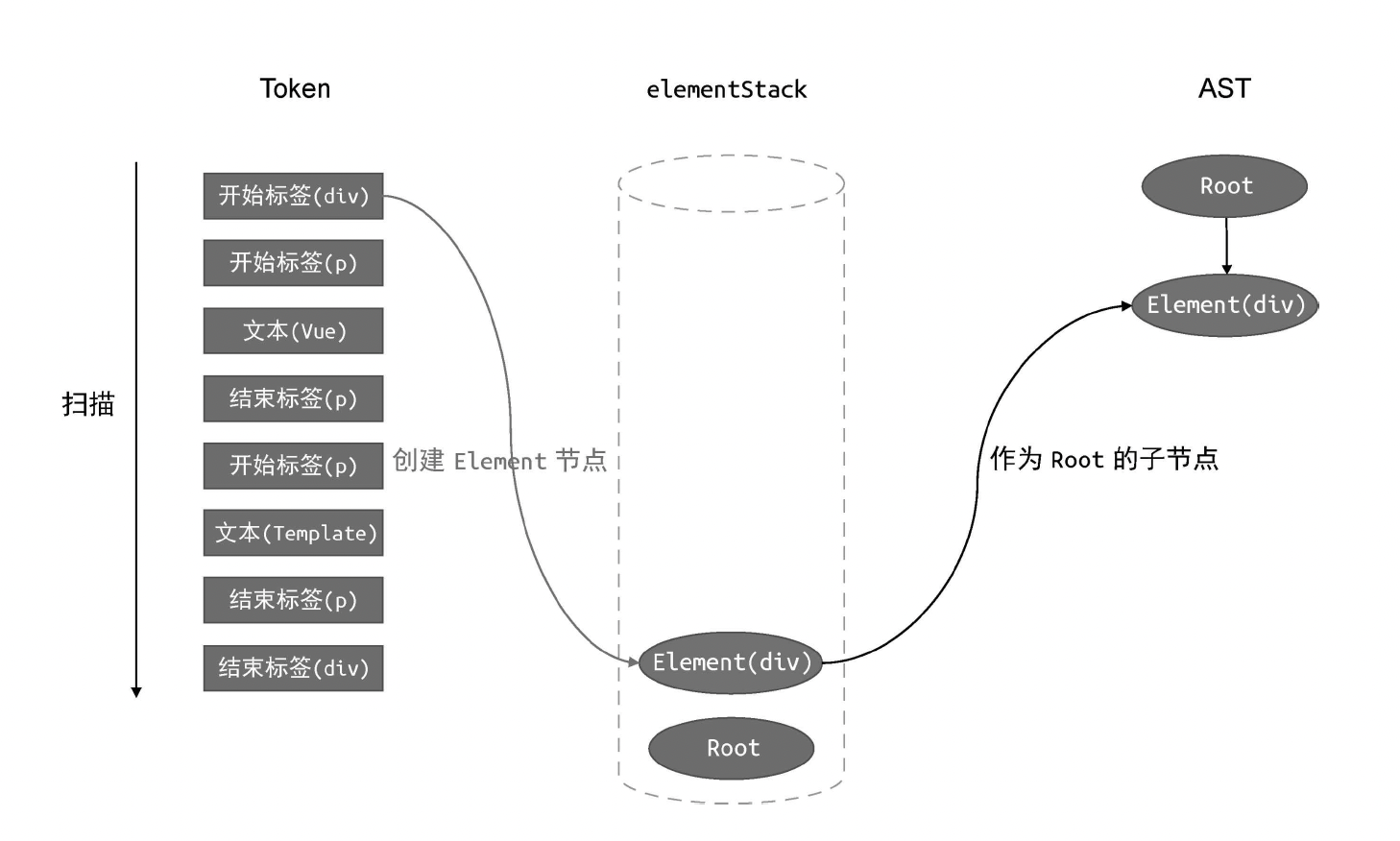
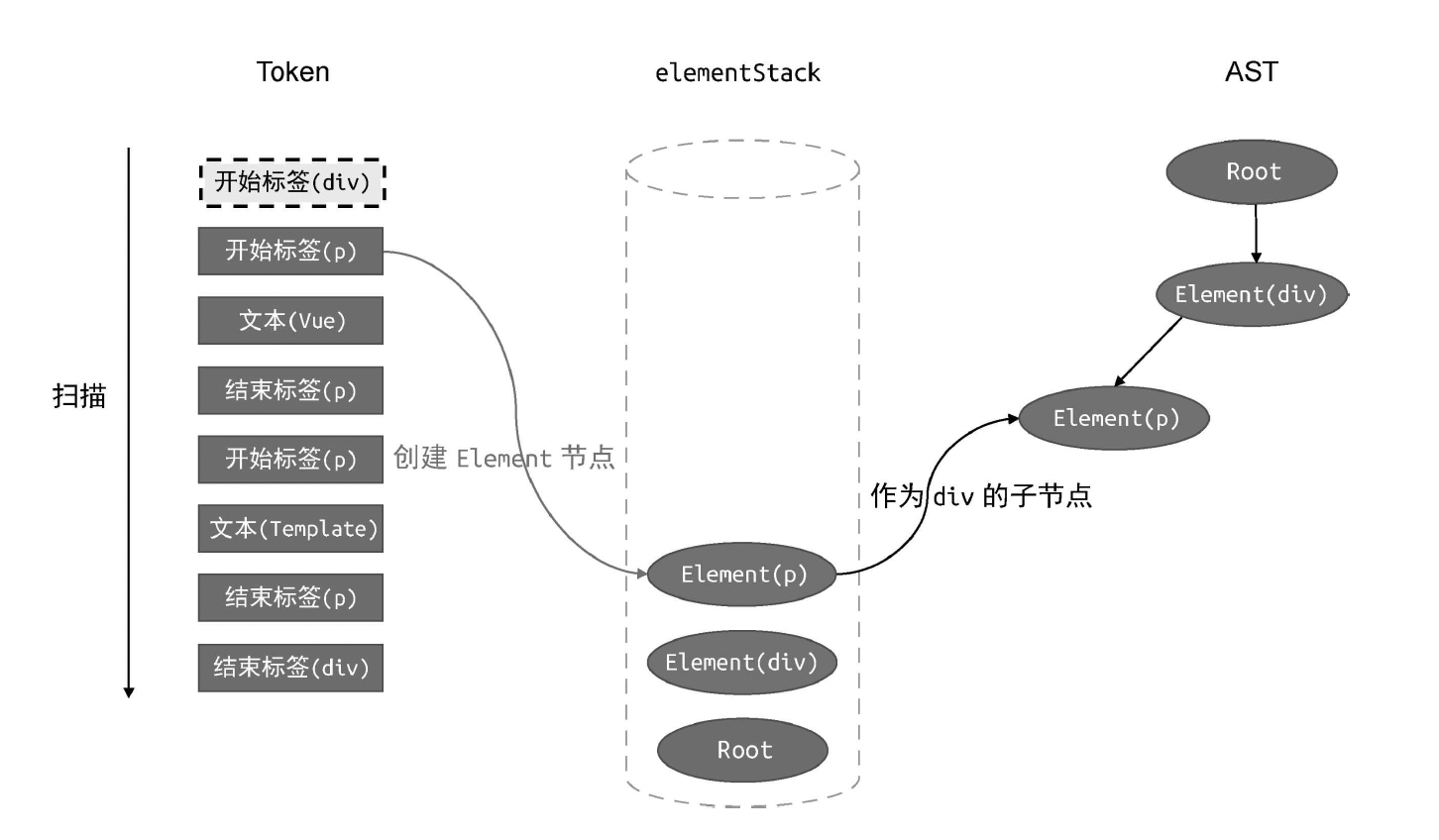
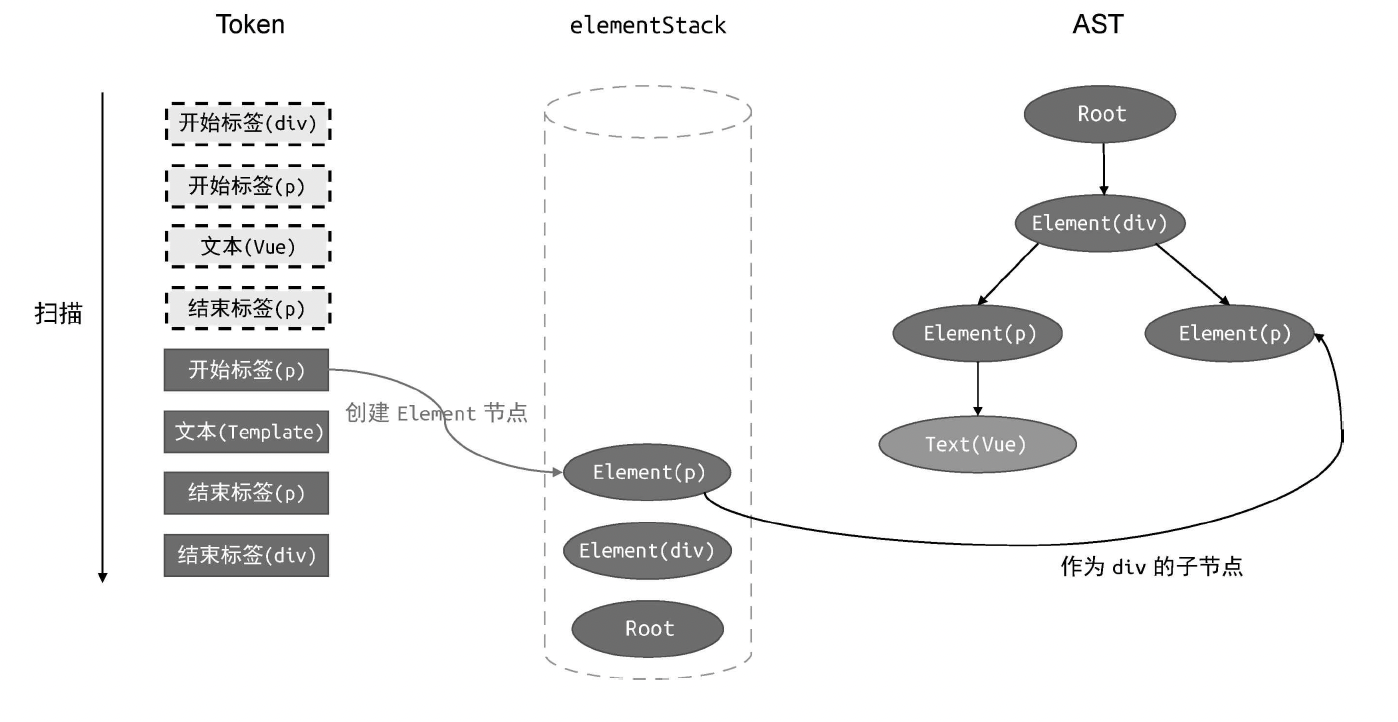
case 'tag':
// 如果当前 Token 是开始标签,则创建 Element 类型的 AST 节点
const elementNode = {
type: 'Element',
tag: t.name,
children: [],
};
// 将其添加到父级节点的 children 中
parent.children.push(elementNode);
// 将当前节点压入栈
elementStack.push(elementNode);
break;
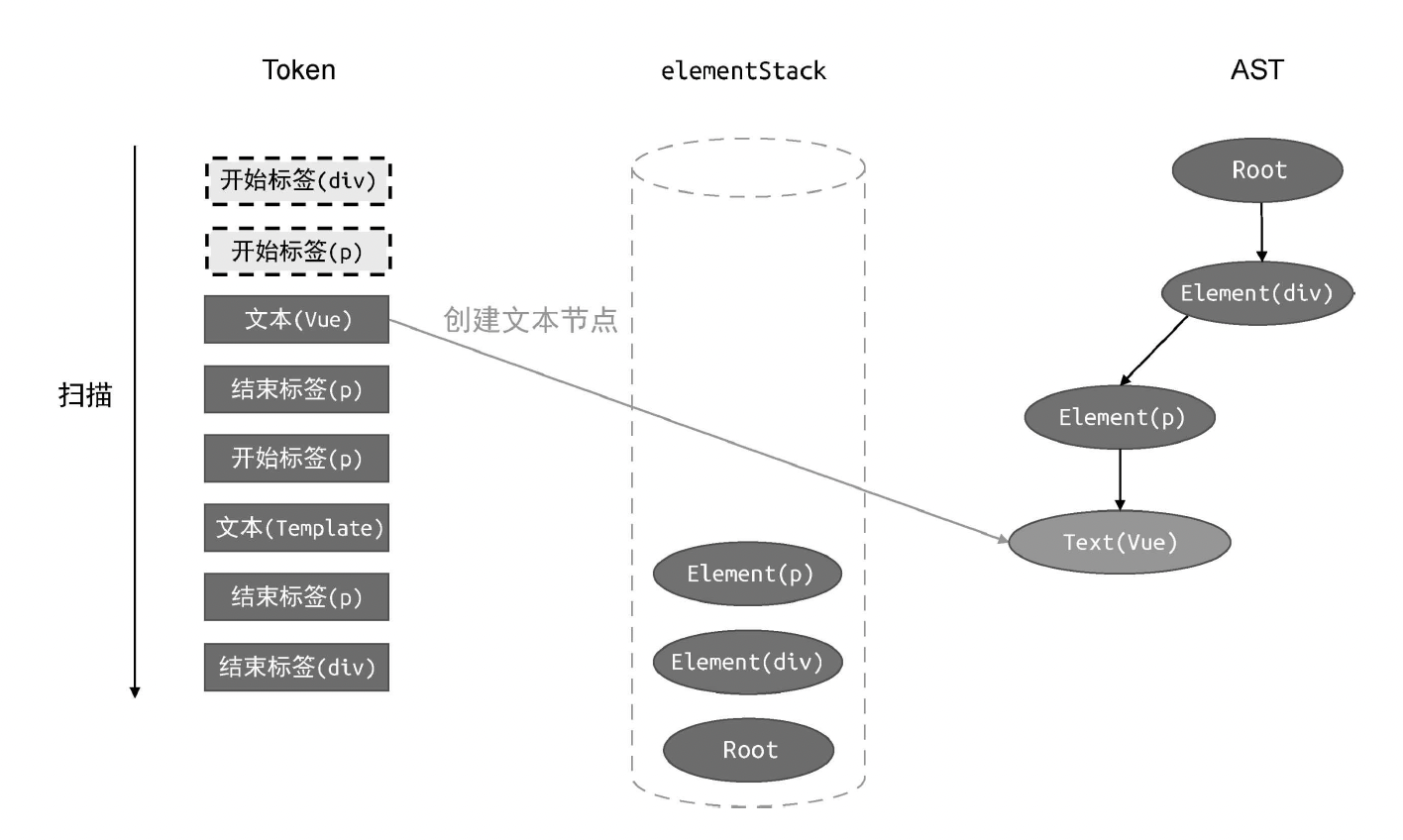
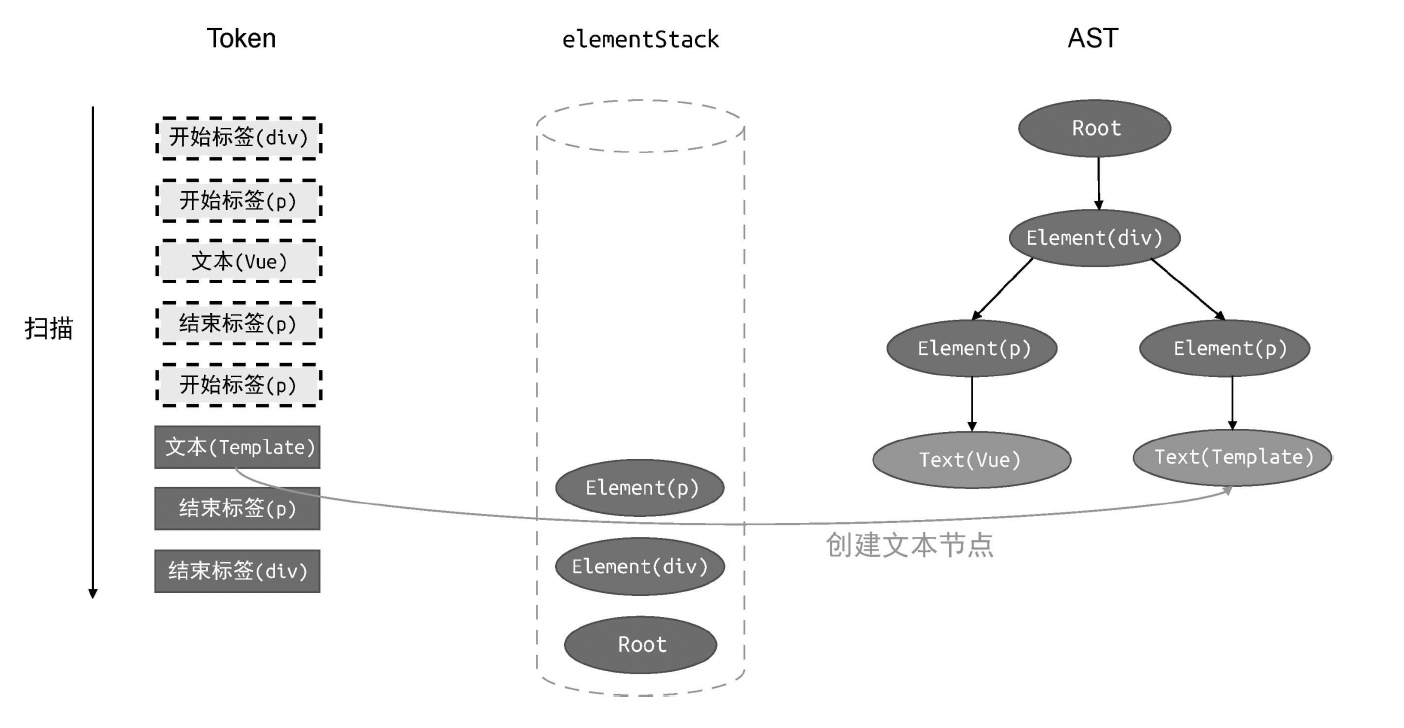
case 'text':
// 如果当前 Token 是文本,则创建 Text 类型的 AST 节点
const textNode = {
type: 'Text',
content: t.content,
};
// 将其添加到父节点的 children 中
parent.children.push(textNode);
break;
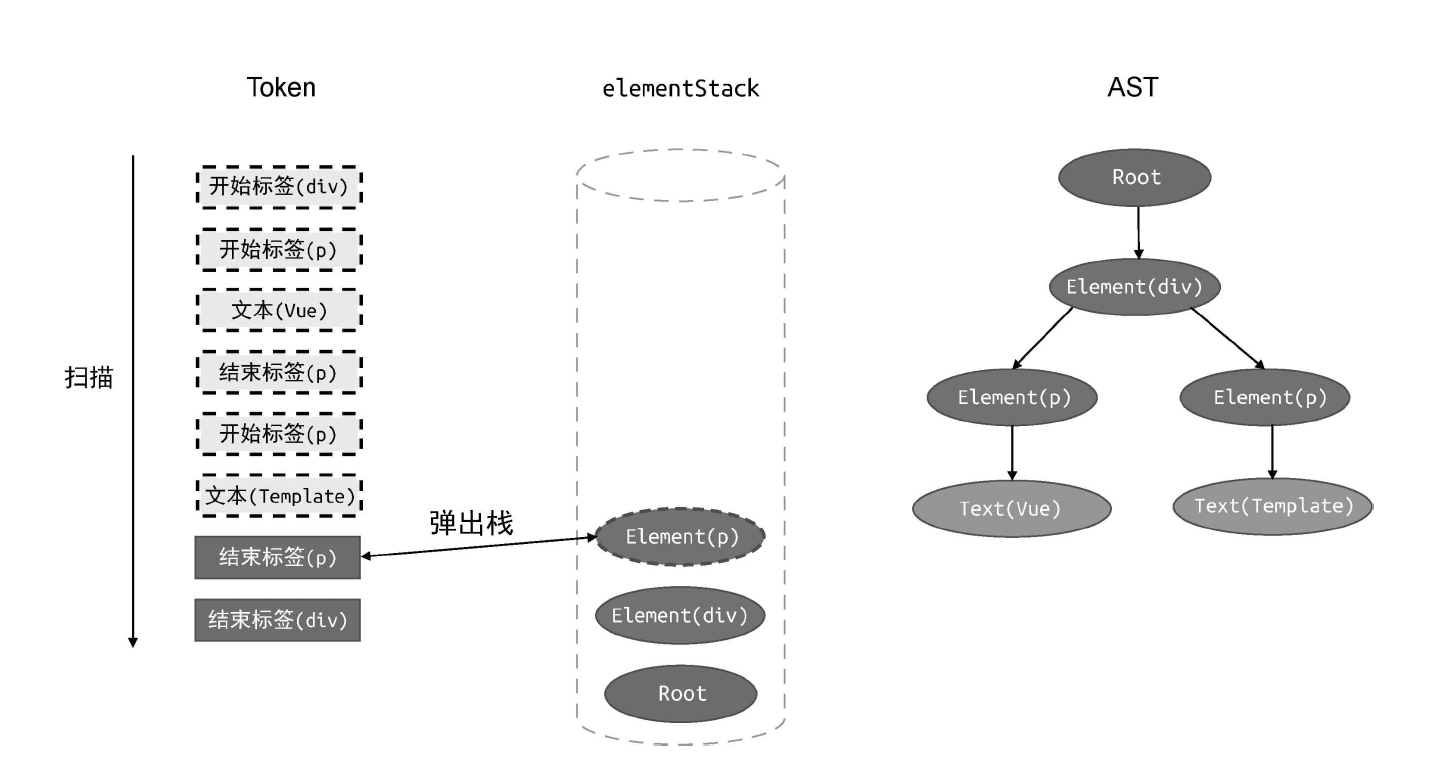
case 'tagEnd':
// 遇到结束标签,将栈顶节点弹出
elementStack.pop();
break;
}
// 消费已经扫描过的 token
tokens.shift();
}
// 最后返回 AST
return root;
}// parse 函数接收模板作为参数
function parse(str) {
// 首先对模板进行标记化,得到 tokens
const tokens = tokenize(str);
// 创建 Root 根节点
const root = {
type: 'Root',
children: [],
};
// 创建 elementStack 栈,起初只有 Root 根节点
const elementStack = [root];
// 开启一个 while 循环扫描 tokens,直到所有 Token 都被扫描完毕为止
while (tokens.length) {
// 获取当前栈顶节点作为父节点 parent
const parent = elementStack[elementStack.length - 1];
// 当前扫描的 Token
const t = tokens[0];
switch (t.type) {
case 'tag':
// 如果当前 Token 是开始标签,则创建 Element 类型的 AST 节点
const elementNode = {
type: 'Element',
tag: t.name,
children: [],
};
// 将其添加到父级节点的 children 中
parent.children.push(elementNode);
// 将当前节点压入栈
elementStack.push(elementNode);
break;
case 'text':
// 如果当前 Token 是文本,则创建 Text 类型的 AST 节点
const textNode = {
type: 'Text',
content: t.content,
};
// 将其添加到父节点的 children 中
parent.children.push(textNode);
break;
case 'tagEnd':
// 遇到结束标签,将栈顶节点弹出
elementStack.pop();
break;
}
// 消费已经扫描过的 token
tokens.shift();
}
// 最后返回 AST
return root;
}结果
js
const ast = parse(`<div><p>Vue</p><p>Template</p></div>`);
ast = {
type: 'Root',
children: [
{
type: 'Element',
tag: 'div',
children: [
{
type: 'Element',
tag: 'p',
children: [{ type: 'Text', content: 'Vue' }],
},
{
type: 'Element',
tag: 'p',
children: [{ type: 'Text', content: 'Template' }],
},
],
},
],
};const ast = parse(`<div><p>Vue</p><p>Template</p></div>`);
ast = {
type: 'Root',
children: [
{
type: 'Element',
tag: 'div',
children: [
{
type: 'Element',
tag: 'p',
children: [{ type: 'Text', content: 'Vue' }],
},
{
type: 'Element',
tag: 'p',
children: [{ type: 'Text', content: 'Template' }],
},
],
},
],
};过程